For more information, you can take a look at my search engine optimization course
In order for a specific URL to show up, when searching in Google’s index it has to be discovered. This is the main purpose of the crawling process. So when a particular web site is being submitted to Google for indexing the crawler first fetches its main entry point which is usually index.html file and then it tries to discover as much as possible internal pages following the web page links. Next for each discovered page the crawler makes an HTTP request just like you do in a browser and parses all the found content so it can gather readable information.
The process of parsing includes: removing all the HTML tags, scripts, styles and the so-called “stop words”. Stop words usually represent commonly used words and just because they bring noise to the information they are being discarded. After the cleanup, algorithms of machine learning are trying to understand the topic of the content based on information they have learned from previous websites.
You may ask yourself what does the Google index look like?
Although the real index and all the factors which Google takes into account before ranking a web page for a specific keyword remain a secret. We could represent the index as a table-like distributed database structure which holds the following columns: term or keyword and path to a document (from the website documents) where the keyword is found. In other words, this table is used to map the relevance of the keyword towards a particular web document, so in a case of search, the search engine could easily determine where (in which document) a specific word could be found. Now that we have a grasp on the index structure let’s take a look at the actual process of Indexing:
The search engine performs two main tasks: first is to find meaningful words from the parsed content related to its topic and the second is to associate them together with the path to the document in its existing index.
You may ask how the engine knows if a particular keyword is relevant?
The local relevancy of a word or a combination of words for a particular document is calculated using techniques such as Inverted index, Latent Semantic Indexing, and others:
- The Inverted index is a data structure where all the unique words found in a document are mapped to a list of documents where they also appear.
- In LSI the mapping additionally considers relations between keywords and concepts contained in a collection of text documents.
One more thing: in this process, you have to know that all the cached copies of the documents are archived and stored in another place.
Crawling and indexing continued
There are ways to control the crawler’s access to a website as well as to choose which pages to be taken into account for indexing. This can be done by placing a meta tag in the head section of a particular web page as well as by creating and using a robots.txt file inside the website’s root directory.
There are two properties: index and follow which are related to indexing and crawling processes that we will discuss:
Meta: index says that the page should be added to the index database.
Meta: follow controls crawling of the inner links inside the web page.
If we would like to restrict the crawler’s access to content we would use “nofollow” attribute.
If we would like the web page not to be a part of the search engine index, and to be excluded from the search results we use the “noindex” attribute.
The robots.txt file is primarily used for excluding crawling of a web page. It is a text file containing information on which pages/domains/directories to be included/or excluded from a particular website. It is one per website and resides in its root directory.
Robots.txt example:
# Rule 1 User-agent: Googlebot Disallow: /nogooglebot/ # Rule 2 User-agent: * Allow: /
Now let's see the difference between using robots.txt and meta tags with an example of crawl blocking.
The next example is showing how we can have a website but some of its web pages to continue displaying: A description for this result is not available because of this site’s robots.txt file.
First, let's discuss why we are having this situation. Apparently, this website has in its description the tag: meta robots=”index” so it has been indexing appropriately,
but in the robots.txt file we have disallowed this web page, so it's denying the display of the description of the result. In this way, the web page is added to the index (have been discovered), but has not being crawled (link index)
Before proceeding with the next examples, lets first be clear on what is link juice?
It is actually the value passed from one page or site to another through hyperlinks. Search engines see it as a vote or a signal by other pages that the page they are linking to is valuable.
In the figure on the left side, you can see how one page can pass link juice to another.
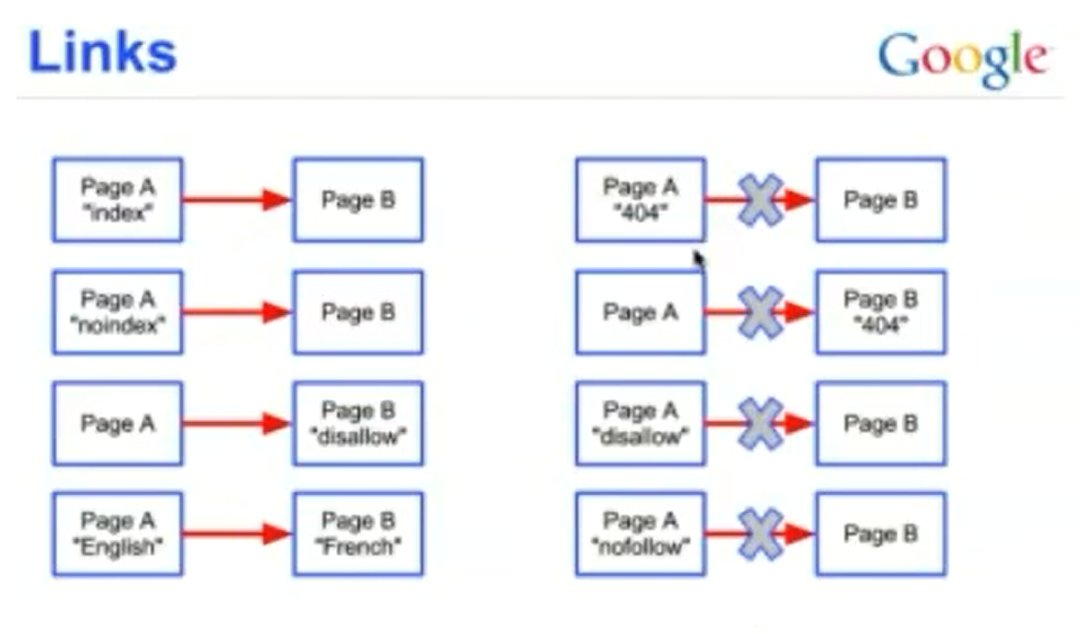
- If the main page returns 404 or not found, its link juice will not be calculated and transferred to the other page.
- If the page we are linking to cannot be found also the link juice remains in the source page
For the next two cases, we have to see what does ...robots.txt file example photo
do. It is a plain text document file, where we can describe directories and files to be allowed or disallowed from crawling when a particular search engine visits our website.
- When a page is disallowed in the robots.txt file its internal links would not be passing link juice to the destination page
- And finally, if a page has a “nofollow” attribute placed on the link, the link will not flow it to the destination page.
This update main goal is to prevent the exchange of bad linking practices between websites. Such schemes are used by SEO 'specialists' in order to increase a particular website reputation. As well as in reverse direction, to negatively affect specific website by having lots of low-quality website links pointing to the targeted website. Here is how to clean up such situations. We can go to the search console and from there to see who is linking to us. Then we check all the listed domains by hand for issues. Other free websites that are also very helpful for finding back-linking sites are NeilPatel's website as well as backlinkwatch. After obtaining the spammy websites list we just create a plain text file disavow.txt where we place all the links following the format: domain: spammy.com. The last step is to upload the file to google's disavow tool. You will have to wait some days before the penalty imposed by this kind of negative SEO will be released.
Panda/topical/quality update
This penalty affects the entire website and even a single webpage could cause it.
Here are a few ways on how to remedy the situation if your website is being targeted by the Panda update:
If you have very similar articles just merge them or add more relevant content to the shorter ones. For articles aim for having about 1000 words of content.
In order to identify what might be the source of the problem, especially if you have lots of pages, you can group your categories into subdomains. Then the search console, will allow you to inspect them by domain so you can gain insight into which categories perform better and decide whether to correct the weak pages or just disallow the whole category. You can become even more granular by using sitemaps of the whole site pages. After submitting the sitemap in search console, you will have information on which pages are being fully indexed and which are having problems. The benefit of this technique is that it will show you which categories are not performing well to the level of individual URLs.
In case you have an article which spans in multiple pages, you can add rel next and rel prev inside your HTML markup, so Google can treat those pages as a group of pages.
More techniques:
First, identify the top 5 pages receiving most impressions and at the same time having very low CTR (clicks). The improvement action in such a case for you is just to correct their meta description and title in order to help them become more attractive to the visitors.
Transfer power from higher to lower-ranking pages, or just analyze the good rank pages and how they differ from the lower-ranking pages. When done you can either delete the weak pages or merge them into the powerful pages.
For comments: choose to be displayed only after a user performs an action such as clicking on a button. On one hand this improves the UI and on other it prevents SPAM. In many cases webmasters choose just to disallow commenting on pages altogether.
The most effective yet longest technique for dealing with the Panda update is to allow only high-quality pages inside the Google index. Start with a few ones which already have good click-through rate and impressions, and then gradually allow more pages to the quality indexed list by rewriting, updating or adding new information inside.
Top-heavy update
The update targets websites that use too much of an advertisement inside the first screen a particular user sees. This way you might have great content, but if it is being occupied with advertisement the penalty will be triggered.
The suggestions in such cases are to have only: 1 ad above the fold (before reaching the vertical scroll height), and it should be of less than 300x250px and 1 per page (for mobile devices). The alternative is to use the auto ad placement available from Google Adsense.
